* Wrote a new module that allows database upgrades via the admin dashboard. * Added a new table t_version that allows to check the version of the database. * The upgrade path is for vanilla databases. It exports and backups data, then reintegrates it.
Labertasche
A comment system for Hugo, written in Python (and Javascript).
Feature Set
- Written in Python, utilizing Flask
- Robust Database handling by utilizing SQLAlchemy, which supports all big database engines
- flask-cors for robust security
- Uses Javascript to send comment via POST to the comment server
- Has callbacks for implementing your own notifications during the posting process.
- No IP being logged
- Email confirmation
- EMail Blocklist
- Only outputs JSON, so templates can be done independently, enhancing customization. Using the comments via a partial template in Hugo is the recommended way. See below for integration code.
- Antispam
- Email Validation
Requirements
- A public webserver capable of running Python, Apache/NGINX and/or gunicorn. This server does not need to be the same as the server running the site, but it must have access to your CI/CD chain. Same server is of course easier to implement.
Dependencies
- Python 3.8
- flask
- flask-cors
- flask-sqlalchemy
- flask-login
- antispam
- pyyaml
- requests
- py3-validate-email
- Recommended OS: Ubuntu 20, Debian Buster
- Recommended Server Software: Apache with libmodwsgi for Python 3
- GoHugo, but the json can also be used by Javascript and other languages
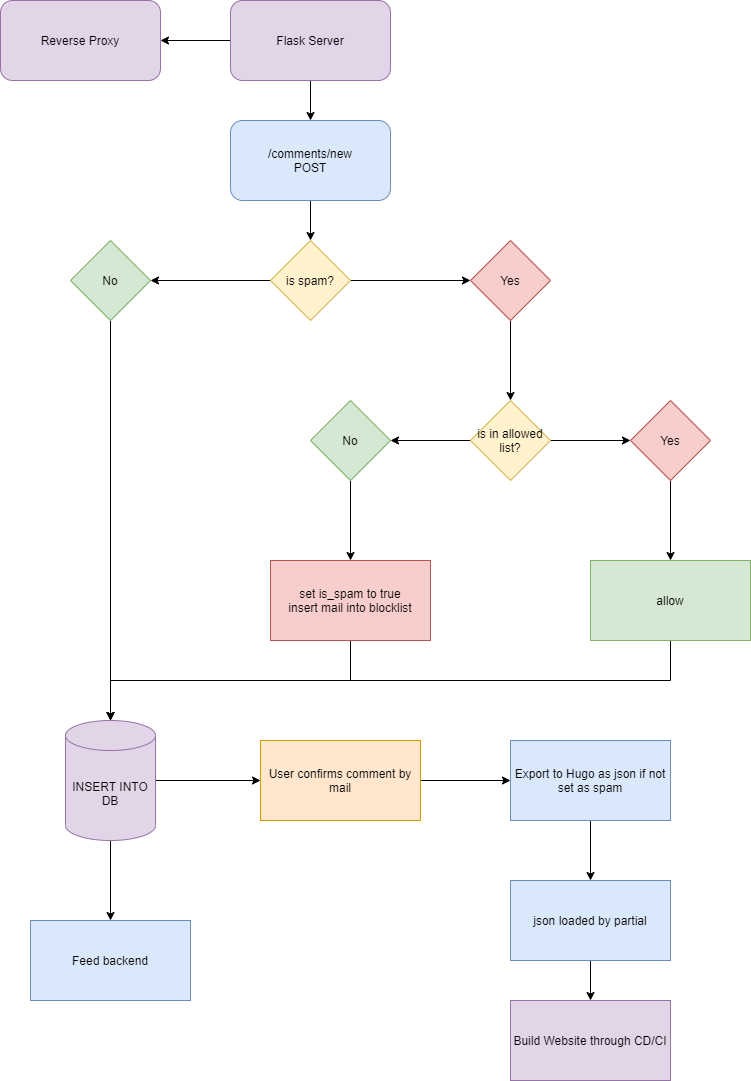
How does it work?
A picture often says more than a thousand words:
In some words, the user sends the comment from your site to the comment system, the comment system does the validation and confirmation. Then, a json is put into the data directory from where you can load it via Hugo and generate your template.
Setup
Run git clone ssh://git@git.tuxstash.de:1235/gothseidank/labertasche.git in the directory where you wish to host the comment
system. For example, /var/www/html, I also recommend making use of /srv/ or /opt/. It depends on you.
When everything is downloaded, create the directory /etc/labertasche. In this directory, we need 2 files:
- labertasche.yaml - you can find an example in the root directory.
- mail_credentials.json - you can find an example in the root directory.
Copy these files from the root directory of this app to the folder /etc/labertasche. Make sure to set ownership for
your user that runs your server later. I always do chown user:www-data, so Apache has only group rights and enable read-only
for the Apache user. I also recommend chmod 700 for the directory and chmod 600 for the files.
Make sure to read the config and replace the values as needed. The mail configuration should need no explanation,
labertasche.yaml has comments. Feel free to bug me about more documentation regarding this. Pay special attention to
secrets and passwords.
Now, for the server there are several options. I personally always host flask apps with Apache and libmodwsgi. The config looks like this:
Other options:
- gunicorn + Apache/Nginx with Proxy Pass
Once you can see the administrative page, you can start integrating it into Hugo.
Integrating it into Hugo
Javascript
In the project folder is a small javascript file. You will need to add this to Hugo. I suggest using Hugo's asset pipeline to integrate it into your site and merge it with your current javascript. One thing is important to know: this script only does the bare bones post request to the comment backend. Any frontend work must be done by yourself, such as messages about minimum length etc. But don't worry: The function is making use of a callback, where you can receive various messages with error codes and act on them. See the javascript file for an example callback.
Hugo templates
Remember the labertasche.yaml file? It asked you where the data folder of Hugo is. What this program does, is to place
various json files into that folder, in folders that describe your sections. So, for each category/section of your blog
where comments can be placed, one folder will be made. And for each page within that section it generates a json file.
Now create a new partial called "comments.html" (or something else). Within that template the following structure is needed:
{{ $location := .Scratch.Get "location" }}
{{ if (fileExists $location ) }}
{{ $dataJ := getJSON $location }}
{{ range $dataJ.comments }}
{# HTML and template codes here #}
{# This is to display replies to this comment, you can use them same variables #}
{{ range where $dataJ.replies "replied_to" .comment_id }}
{# HTML and template codes here for replies #}
{{end}}
{{ end }}
{{ end }}
This loads the json depending on the rel url and walks the list of comments. You can then use the following variables to access the per-comment data:
- .content => The body of the message the user has sent
- .email => The mail the person used to send the mail
- .created_on => The date and time the comment was posted
- .comment_id => The comment id, great for making anchors
- .gravatar => The md5 hash of the mail for gravatar, if caching is on, prepend e.g.
/images, otherwise use the gravatar url to integrate it.
You can style around them as needed. You have free reign.
Of course you will also need a few inputs and a button that submits the data. Here is a base skeleton to start out:
<di id="labertasche-comment-section" data-remote="https://comments.example.com/comments/new">
<input type="text" maxlength=100 placeholder="Enter Email" id="labertasche-mail">
<textarea cols="10" rows="10" id="labertasche-text"></textarea>
<input type="button" onclick="labertasche_post_comment(this, labertasche_callback);">
</div>
This is the recommended element on each top post if you want to utilize replies:
<div class="">
<a href="#labertasche-comment-section"
onclick="labertasche_reply_to({{.comment_id}}, labertasche_reply_callback);">
reply
</a>
</div>
Please take note of the id on each element, these are mandatory, as well as the function call for the onclick event.
Again, style as needed and add more Javascript to your gusto. Make sure to implement the callback, otherwise the
Javascript will crash. The data-remote= needs to have the URL where you host this program, as well as the path to
the API endpoint.
Inside your template single.html, or wherever you want to place comments, you will also need this:
{{ $file := replaceRE "^(.*)[\\/]$" "data$1.json" .Page.RelPermalink }}
{{ .Scratch.Set "location" $file }}
{{ partial "partials/comments" . }}
There is no styling needed for this part!
After that and configuring labertasche correctly, the json files should be placed in your data folder and all you got to do after that, is to rebuild Hugo and the new comment should appear.
Watching for changes via systemd
Hugo accepts the --watch command without the server option:
hugo --watch is valid and it will watch the directory and rebuild the files, if something changes.
Knowing that, we can build a systemd service from that, which could look like this:
[Unit]
Description=Hugo
After=syslog.target
After=network.target
[Service]
RestartSec=2s
Type=simple
User=www-data
Group=www-data
WorkingDirectory=/var/www/html/
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/hugo --watch --minify --noChmod --cleanDestinationDir --gc
Restart=always
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
-noChmod is a very important switch for this, because it stops Hugo from adjusting the file permissions.
This comes in handy if you have a difference in user and group on your web server. --cleanDestinationDir and --gc
will clean old files out, so you don't have to worry about synching the public directory with the current content of
your static or assets dir. There will also be no old CSS files be lying around when using fingerprinting.